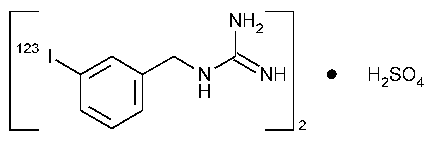
Iobenguane I123Injection
[[3-(Iodo-123I)-phenyl]methyl]guanidine sulfate (2:1).
(m-Iodo-123I)-benzyl)guanidine sulfate (2:1) [139755-80-9].
»Iobenguane I123Injection is a sterile solution containing iobenguane sulfate in which a portion of the molecules contain radioactive iodine (123I)in the molecular structure.Iobenguane I123Injection contains not less than 90.0percent and not more than 110.0percent of the labeled amount of I123as iobenguane expressed in megabecquerels (or in millicuries)per mLat the time indicated in the labeling.It contains not less than 90.0percent and not more than 110.0percent of the labeled amount of iobenguane.It may contain preservatives or stabilizers.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in single-dose or in multiple-dose containers that are adequately shielded.Store in a freezer.
Labeling—
Label it to include the following:the time and date of calibration;the amount of 123Ias iobenguane expressed as total megabecquerels (or millicuries)per mLat the time of calibration;the name and quantity of any added preservative or stabilizer;the expiration time;and the statement “Caution—Radioactive Material.”The labeling indicates that in making dosage calculations,correction is to be made for radioactive decay,and also indicates that the radioactive half-life of 123Iis 13.2hours.
Radionuclidic identification (see Radioactivity á821ñ)—
Its gamma-ray spectrum is identical to that of a specimen of 123Iof known purity that exhibits a major photopeak having an energy of 159KeV.
Bacterial endotoxins á85ñ—
It contains not more than 175/VUSP Endotoxin Unit per mLof the Injection,when compared with the USP Endotoxin RS,in which Vis the maximum recommended total dose,in mL,at the expiration time.
pHá791ñ:
between 6.0and 7.5.
Radionuclidic purity—
Using a suitable counting assembly (see Selection of a Counting Assemblyunder Radioactivity á821ñ),determine the radionuclidic purity of the Injection:not less than 97%of the total radioactivity is present as 123I.
Radiochemical purity—
METHOD
1(High-pressure liquid chromatographic method)—
Mobile phase,Standard preparation,and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay for iobenguane sulfate,except that the liquid chromatograph is also equipped with a collimated radiation detector (see Radioactivity á821ñ).
Test preparation—
Use Iobenguane I123Injection.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 20µL)of Injection,equivalent to 1.6to 2.7MBq (44to 64µCi)of the Injection into the chromatograph,record the chromatogram,and measure the areas for the major peaks.The radioactivity of the iobenguane 123Ipeak is not less than 90%of the total radioactivity measured,and its retention time is within 10%of that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparationobtained in the Assay for iobenguane sulfate.
METHOD
2(Thin-layer chromatographic method)—Apply 0.2to 0.4µLof the Injection 10mm from one end of a 20-×200-mm silica gel glass plate (see Chromatography á621ñ),and allow to dry.Develop the chromatogram by ascending chromatography until the solvent front has moved 100mm from the origin (about 20minutes),using a solvent system consisting of a mixture of alcohol,ethyl acetate,and ammonium hydroxide (20:20:1).Air-dry the chromatogram,and determine the radioactivity distribution by scanning the chromatogram with a collimated radiation detector:not less than 90%of the total radioactivity is found as 123Iat the origin.
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements under Injections á1ñ,except that the Injection may be distributed or dispensed prior to the completion of the test for Sterility á71ñ,the latter test being started on the day of final manufacture,and except that it is not subject to the recommendation on Volume in Container.
Assay for iobenguane sulfate—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water and acetonitrile (900:100).Add 3.04g of triethylamine per liter,and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pHof 4.Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitabilityunder Chromatography á621ñ).
Standard preparation—
Using an accurately weighed quantity of iobenguane sulfate,prepare a solution in water having a known concentration of about 1mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Use the Injection,which has not yet been brought to full volume with bacteriostatic saline.
Chromatographic system
(see Chromatography á621ñ)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 229-nm detector and a 4.6-mm ×25-cm column that contains 10-µm packing L1.The flow rate is about 1.5mLper minute.Chromatograph the Standard preparation,and record the peak responses as directed under Procedure:the column efficiency is not less than 1000theoretical plates,the tailing factor is not more than 1.2,and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20µL)of the Standard preparationand the Assay preparationinto the chromatograph,record the chromatograms,and measure the responses for the major peaks.Calculate the quantity,in mg,of iobenguane sulfate in each mLof the Injection taken by the formula:
C(rU/rS),
in which Cis the concentration,in mg per mL,of iobenguane sulfate in the Standard preparation,and rUand rSare the iobenguane peak responses obtained from the Assay preparationand the Standard preparation,respectively.
Assay for radioactivity—
Using a counting assembly (see Selection of a Counting Assemblyunder Radioactivity á821ñ),determine the radioactivity,in MBq (or µCi),per mL,of the Injection by use of a calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity á821ñ.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Andrzej Wilk,Ph.D.,Senior Scientific Associate
Expert Committee:(RMI)Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents
USP28–NF23Page 1031
Phone Number:1-301-816-8305