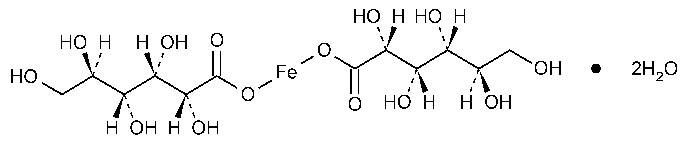
Ferrous Gluconate
D-Gluconic acid,iron(2+)salt (2:1),dihydrate.
Iron(2+)gluconate (1:2)dihydrate [12389-15-0].
Anhydrous 446.15 [299-29-6].
»Ferrous Gluconate contains not less than 97.0percent and not more than 102.0percent of C12H22FeO14,calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
B:
Asolution (1in 200)yields a dark blue precipitate with potassium ferricyanide TS.
Loss on drying á731ñ—
Dry it at 105 for 16hours:it loses between 6.5%and 10.0%of its weight.
for 16hours:it loses between 6.5%and 10.0%of its weight.
Chloride á221ñ—
A1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 1.0mLof 0.020Nhydrochloric acid (0.07%).
Oxalic acid—
Dissolve 1.0g in 10mLof water,add 2mLof hydrochloric acid,and transfer to a separator.Extract successively with 50mLand 20mLof ether.Combine the ether extracts,add 10mLof water,and evaporate the ether on a steam bath.Add 1drop of 6Nacetic acid and 1mLof calcium acetate solution (1in 20):no turbidity is produced within 5minutes.
Sulfate á221ñ—
A1.0-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 1.0mLof 0.020Nsulfuric acid (0.1%).
Arsenic,Method Iá211ñ—
Transfer 1.0g of Ferrous Gluconate to a 100-mL,round-bottom flask fitted with a 24/40standard-taper joint.Add 40mLof 9Nsulfuric acid and 2mLof potassium bromide solution (3in 10).Immediately connect to a suitable distillation apparatus having a reservoir with a water jacket,cooled with circulating ice water,and heat to dissolve the test specimen.Distill,collect 25mLof distillate,and transfer the distillate to the arsine generator flask.Wash the condenser and reservoir several times with small portions of water,add the washings to the distillate in the generator flask,add bromine TSuntil the solution is slightly yellow,and dilute with water to 35mL.Proceed as directed for Procedure:the limit is 3ppm.
Limit of ferric iron—
Dissolve about 5g,accurately weighed,in a mixture of 100mLof water and 10mLof hydrochloric acid,and add 3g of potassium iodide.Shake,and allow to stand in the dark for 5minutes.Titrate any liberated iodine with 0.1Nsodium thiosulfate VS,adding 3mLof starch TSas the endpoint is approached.Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 0.1Nsodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 5.585mg of ferric iron.Ferrous Gluconate contains not more than 2.0%of ferric iron.
Limit of lead—
[NOTE—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glassware before use,employ water that has been passed through a strong-acid,strong-base,mixed-bed ion-exchange resin before use.Select all reagents to have as low a content of lead as practicable,and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass.Clean glassware before use by soaking in warm 8Nnitric acid for 30minutes and by rinsing with deionized water.]
Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution—
Dissolve 20g of ascorbic acid and 38.5g of sodium iodide in water in a 200-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Trioctylphosphine oxide solution—
[Caution—This solution causes irritation.Avoid contact with eyes,skin,and clothing.Take special precautions in disposing of unused portions of solutions to which this reagent is added.
]Dissolve 5.0g of trioctylphosphine oxide in 4-methyl-2-pentanone in a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with the same solvent to volume,and mix.
Standard solution andBlank—
Transfer 5.0mLof Lead Nitrate Stock Solution,prepared as directed in the test for Heavy Metals á231ñ,to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 2.0mLof the resulting solution to a 50-mLvolumetric flask.To this volumetric flask and to a second,empty 50-mLvolumetric flask(Blank)add 10mLof 9Nhydrochloric acid and about 10mLof water.To each flask add 20mLof Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solutionand 5.0mLof Trioctylphosphine oxide solution,shake for 30seconds,and allow to separate.Add water to bring the organic solvent layer into the neck of each flask,shake again,and allow to separate.The organic solvent layers are the Blankand the Standard solution,and they contain 0.0and 2.0µg of lead per mL,respectively.
Test solution—
Add 1.0g of Ferrous Gluconate,10mLof 9Nhydrochloric acid,about 10mLof water,20mLof Ascorbic acid–sodium iodide solution,and 5.0mLof Trioctylphosphine oxide solutionto a 50-mLvolumetric flask,shake for 30seconds,and allow to separate.Add water to bring the organic solvent layer into the neck of the flask,shake again,and allow to separate.The organic solvent layer is the Test solution.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Blank,the Standard solution,and the Test solutionat the lead emission line at 283.3nm,with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering á851ñ)equipped with a lead hollow-cathode lamp and an air–acetylene flame,using the Blankto set the instrument to zero.In a suitable analysis,the absorbance of the Standard solutionand the absorbance of the Blank are significantly different:the absorbance of the Test solutiondoes not exceed that of the Standard solution(0.001%).
Mercury á261ñ:
3ppm.
Reducing sugars—
Dissolve 500mg in 10mLof water,warm,and render alkaline with 1mLof 6Nammonium hydroxide.Pass hydrogen sulfide gas into the solution to precipitate the iron,and allow the solution to stand for 30minutes to coagulate the precipitate.Filter,and wash the precipitate with two successive 5-mLportions of water.Acidify the combined filtrate and washings with hydrochloric acid,and add 2mLof 3Nhydrochloric acid in excess.Boil the solution until the vapors no longer darken lead acetate paper,and continue to boil,if necessary,until it has been concentrated to about 10mL.Cool,add 5mLof sodium carbonate TSand 20mLof water,filter,and adjust the volume of the filtrate to 100mL.To 5mLof the filtrate add 2mLof alkaline cupric tartrate TS,and boil for 1minute:no red precipitate is formed within 1minute.
Organic volatile impurities,Method Iá467ñ:
meets the requirements.
Assay—
Dissolve about 1.5g of Ferrous Gluconate,accurately weighed,in a mixture of 75mLof water and 15mLof 2Nsulfuric acid in a 300-mLconical flask.Add 250mg of zinc dust,close the flask with a stopper containing a Bunsen valve,and allow to stand at room temperature for 20minutes or until the solution becomes colorless.Pass the solution through a filtering crucible containing a thin layer of zinc dust,and wash the crucible and contents with 10mLof 2Nsulfuric acid,followed by 10mLof water.[NOTE—Prepare and use the filtering crucible in a well-ventilated hood.]Add orthophenanthroline TS,and immediately titrate the filtrate in the suction flask with 0.1Nceric sulfate VS.Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 0.1Nceric sulfate is equivalent to 44.61mg of C12H22FeO14.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Lawrence Evans,III,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(DSN)Dietary Supplements:Non-Botanicals
USP28–NF23Page 819
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.29(3)Page 630
Phone Number:1-301-816-8389