á261ñMERCURY
Method I
NOTE—Mercuric dithizonate is light-sensitive.Perform this test in subdued light.
Reagents—
DITHIZONE STOCK SOLUTION—
Dissolve 40mg of dithizone in 1000mLof chloroform.
DITHIZONE TITRANT—
Dilute 30.0mLof Dithizone Stock Solutionwith chloroform to 100.0mL.This solution contains approximately 12mg of dithizone per liter.
MERCURY STOCK SOLUTION—
Transfer 135.4mg of mercuric chloride to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,and dilute with 1Nsulfuric acid to volume.This solution contains the equivalent of 100mg of Hg in 100mL.
MERCURY SOLUTION FOR STANDARDIZING DITHIZONE TITRANT—
Transfer 2.0mLof Mercury Stock Solutionto a 100-mLvolumetric flask,and dilute with 1Nsulfuric acid to volume.Each mLof this solution contains the equivalent of 20µg of Hg.
The following solutions are called for in the limit test for mercury that is specified in the monographs on Ferrous Fumarate,Ferrous Sulfate,and Dried Ferrous Sulfate.
HYDROXYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE SOLUTION—
Prepare as directed in the test for Lead á251ñ.
STANDARD MERCURY SOLUTION—
On the day of use,quantitatively dilute 1.0mLof Mercury Stock Solutionwith 1Nsulfuric acid to 1000mL.Each mLof the resulting solution contains the equivalent of 1µg of mercury.
DITHIZONE EXTRACTION SOLUTION—
Prepare as directed in the test for Lead á251ñ.
DILUTED DITHIZONE EXTRACTION SOLUTION—
Just prior to use,dilute 5mLof Dithizone Extraction Solutionwith 25mLof chloroform.
Standardization of Dithizone Titrant—
Transfer 1.0mLof Mercury Solution for Standardizing Dithizone Titrantto a 250-mLseparator,and add 100mLof 1Nsulfuric acid,90mLof water,1mLof glacial acetic acid,and 10mLof hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution (1in 5).Titrate the solution with Dithizone Titrantfrom a 10-mLmicroburet,shaking the mixture 20times after each addition and allowing the chloroform layer to separate,then discarding the chloroform layer.Continue until a final addition of Dithizone Titrantis green in color after shaking.Calculate the quantity,in µg,of Hg equivalent to each mLof Dithizone Titrantby the formula:
20/V,
in which Vis the volume,in mL,of Dithizone Titrantadded.
Test Preparation—
Transfer about 2g of the substance under test,accurately weighed,to a glass-stoppered,250-mLconical flask,add 20mLof a mixture of equal volumes of nitric acid and sulfuric acid,attach a suitable condenser,reflux the mixture for 1hour,cool,cautiously dilute with water,and boil until fumes of nitrous acid no longer are noticeable.Cool the solution,cautiously dilute with water,transfer to a 200-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,mix,and filter.
Procedure—
Transfer 50.0mLof Test Preparationto a 250-mLseparator,and extract with successive small portions of chloroform until the last chloroform extract remains colorless.Discard the chloroform extract,and add to the extracted Test Preparation50mLof 1Nsulfuric acid,90mLof water,1mLof glacial acetic acid,and 10mLof hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution (1in 5).Proceed as directed under Standardization of Dithizone Titrant,beginning with “Titrate the solution.”Calculate the amount of mercury.
Method IIa and Method IIb
Mercury Detection Instrument—
Use any suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a fast-response recorder and capable of measuring the radiation absorbed by mercury vapors at the mercury resonance line of 253.6nm.[NOTE—Wash all glassware associated with the test with nitric acid,and rinse thoroughly with water before use.]
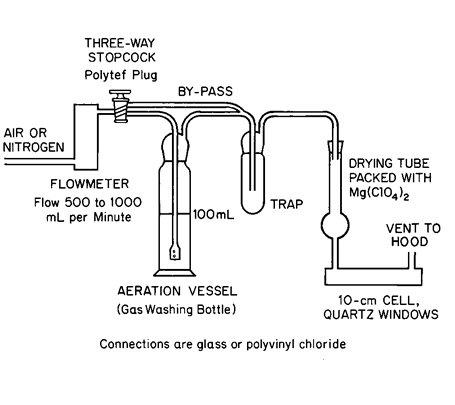
Aeration Apparatus—
The apparatus (see accompanying diagram)consists of a flowmeter capable of measuring flow rates from 500to 1000mLper minute,connected via a three-way stopcock fitted with a polytef plug to an aeration vessel (250-mLgas washing bottle),followed by a trap,a drying tube packed with magnesium perchlorate,a 10-cm ×25-mm flow-through cell with quartz windows,and terminating with a vent to a fume hood.
Reagents—
Potassium Permanganate Solution—
Dissolve 5g of potassium permanganate in 100mLof water.
Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride Solution—
Dissolve 10g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride in 100mLof water.
Stannous Chloride Solution—
Dissolve 10g of SnCl2·2H2Oin 20mLof warm hydrochloric acid,and add 80mLof water.Prepare fresh each week.
Standard Mercury Solution—
Prepare from Mercury Stock Solutionas directed under Method I.Each mLof the Standard Mercury Solutioncontains the equivalent of 1µg of mercury.
Test Preparation—
Unless otherwise directed in the individual monograph,use the quantity,in g,of the test substance calculated by the formula:
2.0/L,
in which Lis the mercury limit,in ppm.
Method IIa
Standard Preparation—
Pipet 2.0mLof Standard Mercury Solutioninto a 100-mLbeaker,and add 35mLof water,3mLof sulfuric acid,and 1mLof potassium permanganate solution.Cover the beaker with a watch glass,boil for a few seconds,and cool.
Test Preparation—
Transfer the calculated amount of the test substance to a 100-mLbeaker,and add 35mLof water.Stir,and warm to assist solution,if necessary.Add 2drops of phenolphthalein TS,and,as necessary,slowly neutralize with constant stirring,using 1Nsodium hydroxide or 1Nsulfuric acid.Add 3mLof sulfuric acid and 1mLof Potassium Permanganate Solution.Cover the beaker with a watch glass,boil for a few seconds,and cool.
Procedure—
Assemble the Aeration Apparatusas shown in the accompanying diagram,with the aeration vessel and the trap empty,and the stopcock in the bypass position.Connect the apparatus to the absorption cell,and adjust the air or nitrogen flow rate so that,in the following procedure,maximum absorption and reproducibility are obtained without excessive foaming in the test solution.Obtain a smooth baseline reading at 253.6nm,following the manufacturer's instructions for operating the instrument.
Treat the Standard Preparationand the Test Preparationsimilarly,as follows.Destroy the excess permanganate by adding Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride Solution,dropwise,until the solution is colorless.Immediately wash the solution into the aeration vessel with water,and dilute with water to 100mL.Add 2mLof Stannous Chloride Solution,and immediately reconnect the aeration vessel to the aeration apparatus.Turn the stopcock from the bypass position to the aerating position,and continue the aeration until the absorption peak has been passed and the recorder pen returns to the baseline.Disconnect the aeration vessel from the apparatus,and wash with water after each use.After correcting for any reagent blank,any absorbance produced by the Test Preparationdoes not exceed that produced by the Standard Preparation.
Method IIb
Caution—Some substances may react with explosive violence when digested with hydrogen peroxide.Exercise safety precautions at all times.
Standard Preparation—
Pipet 2.0mLof Standard Mercury Solutioninto a 125-mLconical flask,add 3mLeach of nitric acid and sulfuric acid,mix,and add an amount of 30percent hydrogen peroxide equal to the total amount used in preparing the Test Preparation.Attach a suitable water-cooled condenser with a standard-taper joint to fit the flask,and reflux the mixture in a fume hood for 1hour.Turn off the water circulating through the condenser,and heat until white fumes appear in the flask.Cool,and cautiously add 10mLof water through the condenser,while swirling the flask.Again heat until white fumes appear,cool,and add an additional 15mLof water.Remove the condenser,and rinse the sides of the flask to obtain a volume of 35mL.Add 1mLof Potassium Permanganate Solution,boil for a few seconds,and cool.
Test Preparation—
Transfer the calculated amount of the test substance to a 125-mLconical flask.Add 5mLeach of nitric acid and sulfuric acid and a few glass beads.Attach a suitable water-cooled condenser with a standard-taper joint to fit the flask,and digest in a fume hood,preferably on a hot plate,and at a temperature not exceeding 120 ,until charring begins.(If additional sulfuric acid is necessary to wet the specimen completely,add it carefully through the condenser,but do not allow the total volume added to exceed 10mL.)After the test substance has been decomposed by the acid,cautiously add,dropwise through the condenser,30percent hydrogen peroxide,allowing the reaction to subside and again heating between drops (add the first few drops very slowly with sufficient mixing,in order to prevent a rapid reaction;discontinue heating if foaming becomes excessive).When the reaction has abated,heat cautiously,rotating the flask occasionally to prevent the specimen from caking on glass exposed to the heating unit.Maintain oxidizing conditions at all times during the digestion by adding small quantities of the hydrogen peroxide solution whenever the mixture turns brown or darkens.Continue the digestion until the organic matter is destroyed,and then reflux the mixture for 1hour.Turn off the water circulating through the condenser,and heat until fumes of sulfur trioxide are copiously evolved and the solution becomes colorless or retains only a light straw color.Cool,and cautiously add 10mLof water through the condenser,while swirling the flask.Again heat until white fumes appear.Cool,and cautiously add 15mLof water.Remove the condenser,and rinse the sides of the flask with a few mLof water to obtain a volume of 35mL.Add 1mLof Potassium Permanganate Solution,boil for a few seconds,and cool.
,until charring begins.(If additional sulfuric acid is necessary to wet the specimen completely,add it carefully through the condenser,but do not allow the total volume added to exceed 10mL.)After the test substance has been decomposed by the acid,cautiously add,dropwise through the condenser,30percent hydrogen peroxide,allowing the reaction to subside and again heating between drops (add the first few drops very slowly with sufficient mixing,in order to prevent a rapid reaction;discontinue heating if foaming becomes excessive).When the reaction has abated,heat cautiously,rotating the flask occasionally to prevent the specimen from caking on glass exposed to the heating unit.Maintain oxidizing conditions at all times during the digestion by adding small quantities of the hydrogen peroxide solution whenever the mixture turns brown or darkens.Continue the digestion until the organic matter is destroyed,and then reflux the mixture for 1hour.Turn off the water circulating through the condenser,and heat until fumes of sulfur trioxide are copiously evolved and the solution becomes colorless or retains only a light straw color.Cool,and cautiously add 10mLof water through the condenser,while swirling the flask.Again heat until white fumes appear.Cool,and cautiously add 15mLof water.Remove the condenser,and rinse the sides of the flask with a few mLof water to obtain a volume of 35mL.Add 1mLof Potassium Permanganate Solution,boil for a few seconds,and cool.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Procedureunder Method IIa.