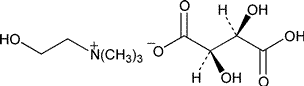
Choline Bitartrate
»Choline Bitartrate contains not less than 99.0percent and not more than 100.5percent of C9H19NO7,calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption á197Kñ.
B:
Dissolve 1g of Choline Bitartrate with 20mLof water,and add 2mLof potassium chloride solution (1in 4).Awhite precipitate of potassium bitartrate is formed.
Specific rotation á781Sñ:
between +17.5 and +18.5
and +18.5 .
.
Test solution:
400mg per mL,in water.
pHá791ñ:
between 3.0and 4.0,in a solution (1in 10).
Water,Method Iá921ñ:
not more than 0.5%.
Residue on ignition á281ñ:
not more than 0.1%.
Arsenic,Method Iá211ñ—
Proceed as directed for Arsenicunder Choline Chloride:the limit is 2µg per g.
Heavy metals,Method IIá231ñ:
10µg per g.
Limit of total amines—
Proceed as directed for Limit of total aminesunder Choline Chloride:not more than 10µg per g.
Test solution—
Transfer 10.0g of Choline Bitartrate to a beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar,add 70mLof sodium hydroxide TSand 130mLof water,and stir until dissolved.
Chromatographic purity—
Buffer solution,Mobile phase,Standard solution,andChromatographic system—
Proceed as directed for Chromatographic purityunder Choline Chloride.
Test solution—
Transfer about 500mg of Choline Bitartrate,accurately weighed,to a centrifuge tube,add 2.0mLof water,and swirl to dissolve.Add 0.5mLof potassium chloride solution (7.5in 25),centrifuge,and transfer 1.0mLof the supernatant to a 24-mLscrew-capped vial.Dry at 120 for 2hours.Add 400mg of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and 10mLof acetonitrile,and mix.Cap the vial,and heat at 55
for 2hours.Add 400mg of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and 10mLof acetonitrile,and mix.Cap the vial,and heat at 55 for 1hour.Cool to room temperature,add 5mLof water,and allow to stand for 2minutes.Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with Mobile phaseto volume,and mix.
for 1hour.Cool to room temperature,add 5mLof water,and allow to stand for 2minutes.Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with Mobile phaseto volume,and mix.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20µL)of the Standard solutionand the Test solutioninto the chromatograph,record the chromatograms,and measure all of the peak responses.Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Choline Bitartrate taken by the formula:
(253.25/139.62)5000(C/W)(ri/rS),
in which 253.25and 139.62are the molecular weights of choline bitartrate and choline chloride,respectively;Cis the concentration of USP Choline Chloride RS,in mg per mL,in the Standard solution;Wis the weight,in mg,of Choline Bitartrate taken to prepare the Test solution;riis the peak response for each impurity,other than that of the choline bitartrate derivative and 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid;and rSis the peak response for the choline chloride derivative in the Standard solution:not more than 0.3%of any individual impurity is found;and not more than 2.0%of total impurities is found.
Organic volatile impurities,Method IVá467ñ:
meets the requirements,except that the limit for 1,4-dioxane is 10µg per g.
Assay—
Transfer about 200mg of Choline Bitartrate,accurately weighed,to a conical flask,and dissolve with 50mLof glacial acetic acid.Titrate with 0.1Nperchloric acid VS,determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see Titrimetry á541ñ).Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 0.1Nperchloric acid is equivalent to 25.32mg of C9H19NO7.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Lawrence Evans,III,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(DSN)Dietary Supplements:Non-Botanicals
USP28–NF23Page 2066
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.30(3)Page 950
Phone Number:1-301-816-8389