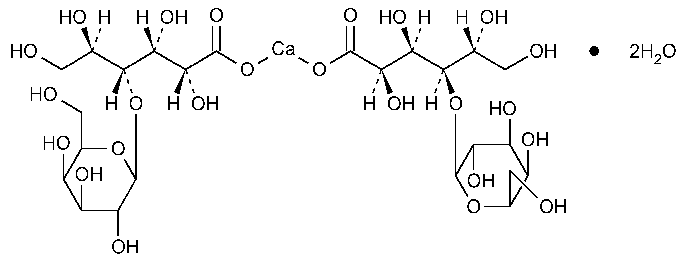
Calcium Lactobionate
D-Gluconic acid,4-O-b-D-galactopyranosyl-,calcium salt (2:1),dihydrate.
Lactobionic acid,calcium salt (2:1),dihydrate.
Calcium lactobionate (1:2),dihydrate [110638-68-1].
»Calcium Lactobionate contains not less than 96.0percent and not more than 102.0percent of C24H42CaO24·2H2O.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Identification—
A:
Asolution (1in 50)responds to the tests for Calcium á191ñ.
C:
Dissolve a quantity of it in water to obtain a test solution containing 10mg per mL.Similarly prepare a Standard solution of USP Calcium Lactobionate RSin water containing 10mg per mL.Apply separately 5µLof the test solution and 5µLof the Standard solution to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography á621ñ)coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel.Dry the plate in a current of cool air.Place the plate in a suitable chromatographic chamber lined with filter paper and previously equilibrated with a solvent system consisting of a mixture of alcohol,water,ethyl acetate,and ammonium hydroxide (50:30:10:10).Develop the chromatogram until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate.Remove the plate from the chamber,and dry at 100 for 20minutes.Allow to cool,and spray with a spray reagent prepared as follows.Dissolve 2.5g of ammonium molybdate in about 50mLof 2Nsulfuric acid in a 100-mLvolumetric flask,add 1.0g of ceric sulfate,swirl to dissolve,dilute with 2Nsulfuric acid to volume,and mix.Heat the plate at 110
for 20minutes.Allow to cool,and spray with a spray reagent prepared as follows.Dissolve 2.5g of ammonium molybdate in about 50mLof 2Nsulfuric acid in a 100-mLvolumetric flask,add 1.0g of ceric sulfate,swirl to dissolve,dilute with 2Nsulfuric acid to volume,and mix.Heat the plate at 110 for about 10minutes:the principal spot obtained from the test solution corresponds in color,size,and RFvalue to that obtained from the Standard solution.
for about 10minutes:the principal spot obtained from the test solution corresponds in color,size,and RFvalue to that obtained from the Standard solution.
Specific rotation á781Sñ:
between +22.0 and +26.5
and +26.5 .
.
Test solution:
100mg per mL,in water.
pHá791ñ:
between 5.4and 7.4,in a solution (1in 20).
Halides—
A1.2-g portion tested as directed under Chloride á221ñshows no more turbidity than corresponds to 0.7mLof 0.020Nhydrochloric acid (0.04%).
Sulfate á221ñ—
A2.0-g portion dissolved in boiling water shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 1mLof 0.020Nsulfuric acid (0.05%).
Heavy metals á231ñ—
Mix 1g with 4mLof 1.2Nhydrochloric acid,add water to make 25mL,warm gently until dissolved,and cool to room temperature:the limit is 0.002%.
Reducing substances—
Transfer 1.0g to a 250-mLconical flask,dissolve in 20mLof water,and add 25mLof alkaline cupric citrate TS.Cover the flask,boil gently for 5minutes,accurately timed,and cool rapidly to room temperature.Add 25mLof 0.6Nacetic acid,10.0mLof 0.1Niodine VS,and 10mLof 3Nhydrochloric acid,and titrate with 0.1Nsodium thiosulfate VS,adding 3mLof starch TSas the endpoint is approached.Perform a blank determination,omitting the specimen,and note the difference in volumes required.Each mLof the difference in volume of 0.1Nsodium thiosulfate consumed is equivalent to 2.7mg of reducing substances (as dextrose):the limit is 1.0%.
Organic volatile impurities,Method Iá467ñ:
meets the requirements.
Assay—
Dissolve about 0.8g of Calcium Lactobionate,accurately weighed,in a mixture of water and 3Nhydrochloric acid (150:2).While stirring with a magnetic stirrer,add about 15mLof 0.05Medetate disodium VSfrom a 50-mLburet.Add 15mLof 1Nsodium hydroxide and 300mg of hydroxy naphthol blue,and continue the titration to a blue endpoint.Each mLof 0.05Medetate disodium is equivalent to 39.53mg of C24H42CaO24·2H2O.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Lawrence Evans,III,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(DSN)Dietary Supplements:Non-Botanicals
USP28–NF23Page 330
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.27(6)Page 3260
Phone Number:1-301-816-8389