á698ñDELIVERABLE VOLUME
The following tests are designed to provide assurance that oral liquids will,when transferred from the original container,deliver the volume of dosage form that is declared on the label of the article.These tests are applicable to products labeled to contain not more than 250mL,whether supplied as liquid preparations or liquid preparations that are constituted from solids upon the addition of a designated volume of a specific diluent.They are not required for an article packaged in single-unit containers when the monograph includes the Uniformity of Dosage Units á905ñtest.
TEST PREPARATIONS
For the determination of deliverable volume,select not fewer than 30containers,and proceed as follows for the dosage form designated.
Oral Solutions,Oral Suspensions,and Other Oral Liquid Dosage Forms—
Shake the contents of 10containers individually.
Powders that are Labeled to State the Volume of Oral Liquid that Results when the Powder is Constituted with the Volume of Diluent Stated in the Labeling—
Constitute 10containers with the volume of diluent stated in the labeling,accurately measured,and shake individually.
PROCEDURE
Being careful to avoid the formation of air bubbles,gently pour the contents of each container into separate dry graduated cylinders of a rated capacity not exceeding two and a half times the volume to be measured,and calibrated “to contain”.Allow each container to drain for a period not to exceed 30minutes,for multiple-unit containers and 5seconds for single-unit containers,unless otherwise specified in the monograph.When free from air bubbles,measure the volume of each mixture.Alternatively,in the case of products of low volume packaged in single-unit containers,the volume can be computed as follows:(1)discharge the container contents into a suitable tared container (allowing drainage for not more than 5seconds);(2)determine the weight of the contents;and (3)compute the volume after determining the density.
ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA
Use the following criteria to determine compliance with this test.
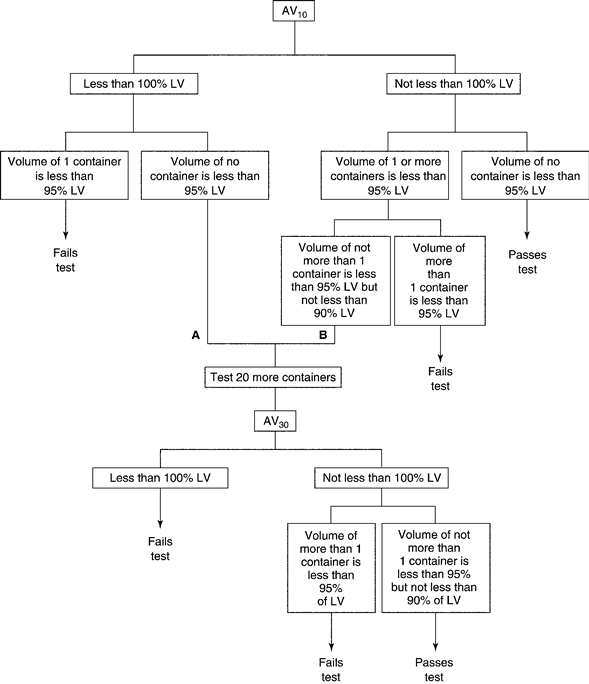
For Multiple-Unit Containers (see Figure 1)—
The average volume of liquid obtained from the 10containers is not less than 100%,and the volume of no container is less than 95%of the volume declared in the labeling.If A,the average volume is less than 100%of that declared in the labeling,but the volume of no container is less than 95%of the labeled amount,or B,the average volume is not less than 100%and the volume of not more than 1container is less than 95%,but is not less than 90%of the labeled volume,perform the test on 20additional containers.The average volume of liquid obtained from the 30containers is not less than 100%of the volume declared in the labeling;and the volume of liquid obtained from not more than 1of the 30containers is less than 95%,but not less than 90%of that declared in the labeling.
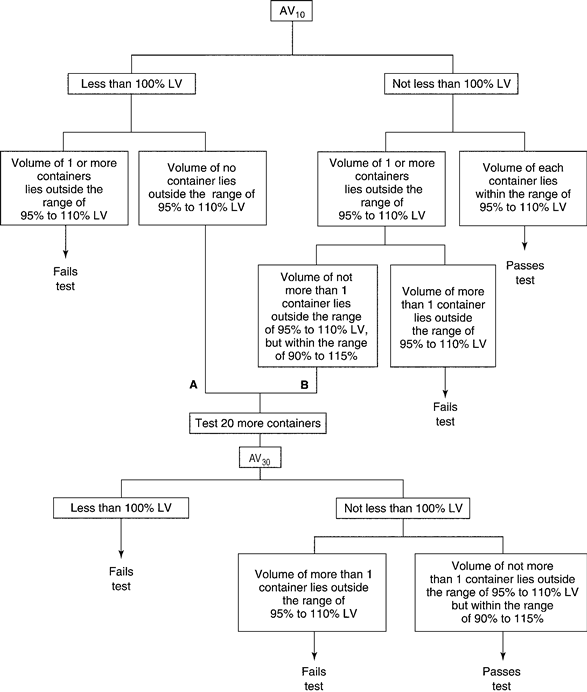
For Single-Unit Containers (see Figure 2)—
The average volume of liquid obtained from the 10containers is not less than 100%,and the volume of each of the 10containers lies within the range of 95%to 110%of the volume declared in the labeling.If A,the average volume is less than 100%of that declared in the labeling,but the volume of no container is outside the range of 95%to 110%,or if B,the average volume is not less than 100%and the volume of not more than 1container is outside the range of 95%to 110%,but within the range of 90%to 115%,perform the test on 20additional containers.The average volume of liquid obtained from the 30containers is not less than 100%of the volume declared in the labeling;and the volume obtained from not more than 1of the 30containers is outside the range of 95%to 110%,but within the range of 90%to 115%of the volume declared on the labeling.