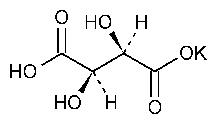
Potassium Bitartrate
Butanedioic acid 2,3-dihydroxy-,[R-(R*,R*)]-,monopotassium salt.
Potassium hydrogen tartrate [868-14-4].
»Potassium Bitartrate,dried at 105 for 3hours,contains not less than 99.0percent and not more than 101.0percent of C4H5KO6.
for 3hours,contains not less than 99.0percent and not more than 101.0percent of C4H5KO6.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
A:
Ignite it:it leaves a residue that imparts a reddish purple color to a nonluminous flame.
B:
Asaturated solution of it yields a yellowish orange precipitate with sodium cobaltinitrite TS.
C:
Asolution (1in 10)responds to the tests for Tartrate á191ñ.
Insoluble matter—
Mix 500mg of it with 3mLof 6Nammonium hydroxide:no undissolved residue remains.
Ammonia—
Heat 500mg of it with 5mLof 1Nsodium hydroxide:no ammonia odor is detected.
Heavy metals,Method Iá231ñ—
Mix 2g of it with 15mLof water,and add 6Nammonium hydroxide dropwise until solution is complete.Add 1drop of phenolphthalein TS,and add just sufficient 1Nacetic acid dropwise to discharge the pink color.Add 2mLof 1Nacetic acid,and dilute with water to 25mL:the limit is 0.002%.
Assay—
Dry about 6g of Potassium Bitartrate at 105 for 3hours,allow to cool,and weigh accurately.Dissolve in 100mLof boiling water,add a few drops of phenolphthalein TS,and titrate with 1Nsodium hydroxide VSto a pink endpoint.Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 1Nsodium hydroxide is equivalent to 188.2mg of C4H5KO6.
for 3hours,allow to cool,and weigh accurately.Dissolve in 100mLof boiling water,add a few drops of phenolphthalein TS,and titrate with 1Nsodium hydroxide VSto a pink endpoint.Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 1Nsodium hydroxide is equivalent to 188.2mg of C4H5KO6.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Elena Gonikberg,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(PA4)Pharmaceutical Analysis 4
USP28–NF23Page 1583
Phone Number:1-301-816-8251