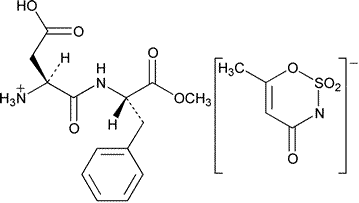
Aspartame Acesulfame
Aspartame acesulfame salt.
[2-carboxy-b-(N-b-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenyl)ethylcarbamo yl)]ethanaminium 6-methyl-4-oxo-1,2,3-oxathiazin-3-ide-2,2-dioxide.
L-Phenylalanine,L-a-aspartyl-2-methyl ester compound with 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide (1:1) [106372-55-8].
»Aspartame Acesulfame contains not less than 63.0percent and not more than 66.0percent of aspartame,calculated on the dried basis.It contains not less than 34.0percent and not more than 37.0percent of acesulfame,calculated as the acid form on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers,and store in a cool,dry place.
USP Reference standards á11ñ—
USP Aspartame Acesulfame RS.USP Aspartame Related Compound A RS.USP Acesulfame Potassium RS.
Identification,Infrared Absorption á197Kñ—
Do not dry specimens.
Transmittance—
The transmittance of a 1in 100solution of Aspartame Acesulfame in distilled water,determined in a 1-cm cell at 430nm with a suitable spectrophotometer,is not less than 0.95.
Specific rotation á781Sñ:
between +14.5 and +16.5
and +16.5 ,determined at 20
,determined at 20 within 30minutes after preparation of the Test solution.Divide the calculated specific rotation by 0.646to correct for the aspartame content in Aspartame Acesulfame.
within 30minutes after preparation of the Test solution.Divide the calculated specific rotation by 0.646to correct for the aspartame content in Aspartame Acesulfame.
15N Formic acid—
To a 1-Lvolumetric flask,add approximately 300mLof water,then weigh 719g of 96%formic acid into this flask,and mix.Cool the solution to 20 .Dilute with water to volume,and mix.
.Dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Test solution:
62mg per mL,in15N Formic acid.
Loss on drying á731ñ—
Dry it at 105 for 4hours:it loses not more than 0.5%of its weight.
for 4hours:it loses not more than 0.5%of its weight.
Residue on ignition á281ñ:
not more than 1.1%.
Heavy metals,Method IIá231ñ:
0.001%.
Limit of potassium—
Potassium stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of about 190mg of potassium chloride,previously dried at 105 for 2hours,in water.Transfer to a 1000-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 100.0mLof this solution to a second 1000-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.This solution contains 10µg of potassium per mL.
for 2hours,in water.Transfer to a 1000-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 100.0mLof this solution to a second 1000-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.This solution contains 10µg of potassium per mL.
Reference solutions—
To three identical 100-mLvolumetric flasks transfer 10.0,15.0,and 20.0mL,respectively,ofPotassium stock solution.To each flask add 2.0mLof sodium chloride solution (1in 5)and 1.0mLof hydrochloric acid,dilute with water to volume,and mix.TheReference solutions contain,respectively,1.0,1.5,and 2.0µg of potassium per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 1.5g of Aspartame Acesulfame,accurately weighed,to a 500-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 10mLof this solution to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,add 2.0mLof sodium chloride solution (1in 5)and 1.0mLof hydrochloric acid,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Filter the solution.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of theReference solutions and theTest solution at the potassium emission line of 766.5nm,with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (seeSpectrophotometry and Light-Scattering á851ñ)equipped with a potassium hollow-cathode lamp and an air–acetylene flame,using water as the blank.Plot the absorbance of theReference solutions versus concentration,in µg per mL,of potassium,and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points.From the graph so obtained,determine the concentration,C,in µg per mL,of potassium in theTest solution.Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken by the formula:
500C/W,
in whichWis the quantity,in mg,of Aspartame Acesulfame taken to prepare theTest solution:not more than 0.5%is found.
Related compounds—
Diluent—
Prepare a mixture of water and methanol (9:1).
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed solution by dissolving 5.6g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 820mLof water in a 1-liter volumetric flask,adjusting with phosphoric acid to a pHof 4.3,diluting with methanol to volume,and mixing.Make adjustments if necessary (seeSystem Suitability underChromatography á621ñ).
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Aspartame Related Compound A RSinDiluent,and quantitatively dilute withDiluent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 25µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer 50mg of Aspartame Acesulfame,accurately weighed,to a 10-mLvolumetric flask,dissolve in and dilute with Diluentto volume,and mix.[NOTE—Avoid heat and excessive holding times.]
Chromatographic system(see Chromatography á621ñ)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 210-nm detector and 4.6-mm ×25-cm column containing packing L1.The flow rate is about 1.5mLper minute.The column temperature is maintained at 40 .Chromatograph theStandard solution,and record the peak responses as directed forProcedure:the tailing factor is not more than 2.0;and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 4.0%.
.Chromatograph theStandard solution,and record the peak responses as directed forProcedure:the tailing factor is not more than 2.0;and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 4.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20µL)of theStandard solution and theTest solution into the chromatograph,record the chromatograms,and measure the responses for the major peaks.Calculate the percentage of aspartame related compound Ain the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken by the formula:
(C/W)(rU/rS),
in whichCis the concentration,in µg per mL,of USP Aspartame Related Compound A RSin theStandard solution;Wis the weight,in mg,of Aspartame Acesulfame,taken to prepare theTest solution;andrUandrSare the peak responses of aspartame related compound Aobtained from theTest solution and theStandard solution,respectively:not more than 0.5%is found.
Chromatographic purity—
Diluent,Mobile phase,Test solution,and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed forRelated compounds.
Acesulfame solution—
Transfer about 20mg of USP Acesulfame Potassium RSto a 10-mLvolumetric flask,dilute withDiluent to volume,and mix.
Diluted test solution—
Pipet 1.5mLof theTest solution into a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute withDiluent to volume,and mix.
Procedure—
Inject equal volumes (about 20µL)of theAcesulfame solution,theDiluted test solution,and theTest solution into the chromatograph,record the chromatograms,and measure the peak responses.[NOTE—Continue the elution of theTest solution for twice the retention time of the aspartame peak.]The sum of the responses of all the peaks in the chromatogram of theTest solution,excluding the aspartame related compound A,acesulfame,and aspartame peak responses,is not greater than the aspartame peak response obtained from theDiluted test solution (1.0%).
Assay—
Accurately weigh about 0.150g of Aspartame Acesulfame,and dissolve in 50mLof dehydrated alcohol.Titrate with 0.1Ntetrabutylammonium hydroxide in methanol/isopropyl alcohol VS.Potentiometrically determine the volumes of titrant,in mL,at the first equivalence point (V1)and at the second equivalence point (V2).Perform a blank titration with 50mLof dehydrated alcohol,and designate the volume of titrant,in mL,asVB.Calculate the percentage of acesulfame and aspartame in the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken by formulas 1and 2,respectively:
163N(V1–VB)/(10W)(1)
294N(V2–V1)/(10W)(2)
in whichNis the normality of the titrant;andWis the weight,in g,of Aspartame Acesulfame taken.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Elena Gonikberg,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(EMC)Excipients:Monograph Content
USP28–NF23Page 2960
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.29(2)Page 453
Phone Number:1-301-816-8251