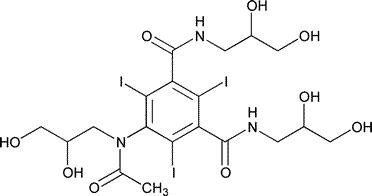
Iohexol
1,3-Benzenedicarboxamide,5-[acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-N,N¢-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo.
N,N¢-Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-[N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide [66108-95-0].
»Iohexol contains not less than 98.0percent and not more than 102.0percent of C19H26I3N3O9,calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed,light-resistant containers.Store at 25 ,excursions permitted between 15
,excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 .
.
USP Reference standards á11ñ—
USP Iohexol RS.USP Iohexol Related Compound A RS.USP Iohexol Related Compound B RS.USP Iohexol Related Compound C RS.
Color of solution—
Transfer 16.18g to a 25-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Pass through a filter having a porosity of 0.22µm.The absorbances of this solution,determined in 1-cm cells at 400nm,420nm,and 450nm,with a suitable spectrophotometer and using water as the blank,are not greater than 0.180,0.030,and 0.015,respectively.
Identification—
A:
The IRabsorption spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion of it exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of a similar preparation of USP Iohexol RS.
B:
The UVabsorption spectrum of a 1in 100,000solution in water exhibits a maximum and a minimum at the same wavelengths as that of a similar solution of USP Iohexol RS,concomitantly measured.
C:
It responds to theThin-layer Chromatographic Identification Test á201ñ,the test solution and the Standard solution of USP Iohexol RSbeing prepared at a concentration of 10mg per mLin methanol,the solvent system being a mixture ofn-butyl alcohol,water,and glacial acetic acid (50:25:11),and short-wavelength UVlight being used to locate the spots.The presence ofexo-andendo-isomers in the test solution is shown by the appearance of two spots,each of which corresponds in size and intensity to the corresponding principal spot,at the sameRFvalue from the Standard solution.The spot having theRFvalue is theendo-isomer.
D:
Heat about 500mg in a crucible:violet vapors are evolved.
Specific rotation á781Sñ:
between –0.5 and +0.5
and +0.5 .
.
Test solution:
50mg per mL,in water.
Water,Method Iá921ñ:
not more than 4.0%.
Heavy metals,Method Iá231ñ:
0.002%.
Free aromatic amine—
Transfer 200mg to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,add 15mLof water,and mix to dissolve.To a second 50-mLvolumetric flask transfer 5mLof water and 10.0mLof a Standard solution prepared by dissolving an accurately weighed quantity of USP Iohexol Related Compound B RSin water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 10µg per mL.To a third 50-mLvolumetric flask add 15mLof water to provide a blank.Place the three flasks in an ice bath,and chill for 5minutes.[NOTE—In conducting the following steps,keep the flasks in the ice bath as much as possible until all of the reagents have been added.]Treat each flask as follows.Add 3.0mLof 5Nhydrochloric acid,and swirl to mix.Add 2.0mLof sodium nitrite solution (1in 50),mix,and allow to stand for 4minutes.Add 2.0mLof sulfamic acid solution (1in 25),shake,and allow to stand for 1minute.[Caution—Considerable pressure is produced.
]
Remove the flasks from the ice bath.To each flask add 2.0mLof a freshly prepared 1in 1000solution of N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in dilute propylene glycol (7in 10),and mix.Dilute with water to volume,mix,and allow to stand for 5minutes.
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the test solution and the Standard solution in 5-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 495nm,with a suitable spectrophotometer,against the blank.The absorbance of the solution from the Iohexol is not greater than that of the Standard solution (0.05%).
Free iodine—
Transfer 2.1g to a 50-mLcentrifuge tube provided with a stopper,add 20mLof water,and shake vigorously to dissolve.[NOTE—The solution may be heated gently to assist in dissolving the sample.Cool to room temperature before proceeding.]Add 5.0mLof toluene and 5mLof 2Nsulfuric acid,shake,and centrifuge at high speed for 15minutes:the toluene layer shows no red or pink color.
Free iodide—
Transfer 5.0g to a suitable container,add about 20mLof water to dissolve,and titrate with 0.001Nsilver nitrate VSusing a silver electrode in combination with an appropriate reference electrode,determining the endpoint potentiometrically.Each mLof 0.001Nsilver nitrate is equivalent to 126.9µg of I(0.001%).
Ionic compounds—
[NOTE—Rinse all glassware five times with distilled water.]Measure the specific resistance,(Rsp),at 20 of a solution in water (1in 50),using a suitable water purity meter.Calculate the specific conductance,k,taken by the formula:
of a solution in water (1in 50),using a suitable water purity meter.Calculate the specific conductance,k,taken by the formula:
(1/Rsp)106.
The specific conductance of the solution is not greater than that of a 0.0002%solution of sodium chloride (equivalent to 0.01%ionic compounds).
Limit of methanol,isopropyl alcohol,and methoxyethanol—
Internal standard solution—
Prepare a solution of secondary butyl alcohol in water containing about 0.05mg per mL.
Reference solution 1—
Transfer about 0.6g of methanol,accurately weighed,to a 1000-mLvolumetric flask,add about 100mLof water,and mix.Add about 0.6g of isopropyl alcohol,accurately weighed,and about 100mLof water,and mix.Add 0.6g of methoxyethanol,accurately weighed,and about 100mLof water,and mix.Dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Reference solution 2—
Transfer 10.0mLofReference solution 1to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 10.0mLof the solution so obtained to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Reference solution 3—
Transfer 5.0mLofReference solution 1to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Reference solution 4—
Transfer 10.0mLofReference solution 1to a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Reference solution 5—
Transfer 10.0mLofReference solution 4and 10.0mLofInternal standard solution to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Transfer 6.0mLof the solution so obtained to a vial fitted with a septum and crimp cap,and seal.Heat the sealed vial at 95 for 15minutes.
for 15minutes.
Test solution 1—
Transfer about 6.25g of Iohexol,accurately weighed,to a 25-mLvolumetric flask.Add 5.0mLofInternal standard solution,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Test solution 2—
Transfer 5.0mLofTest solution 1and 1.0mLof water to a vial fitted with a septum and crimp cap,and seal.Heat the sealed vial at 95 for 15minutes.
for 15minutes.
Test solution 3—
Transfer 5.0mLofTest solution 1and 1.0mLofReference solution 2to a vial fitted with a septum and crimp cap,and seal.Heat the sealed vial at 95 for 15minutes.
for 15minutes.
Test solution 4—
Transfer 5.0mLofTest solution 1and 1.0mLofReference solution 3to a vial fitted with a septum and crimp cap,and seal.Heat the sealed vial at 95 for 15minutes.
for 15minutes.
Test solution 5—
Transfer 5.0mLofTest solution 1and 1.0mLofReference solution 4to a vial fitted with a septum and crimp cap,and seal.Heat the sealed vial at 95 for 15minutes.
for 15minutes.
Chromatographic system(see Chromatography á621ñ)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.53-mm ×30-m fused-silica column coated with a 3-µm phase G43.The carrier gas is helium,flowing at a rate of about 14mLper minute.The chromatograph is programmed as follows.Initially the column temperature is equilibrated at 40 for 5minutes,then the temperature is increased at a rate of 10
for 5minutes,then the temperature is increased at a rate of 10 per minute to 100
per minute to 100 ,and is maintained at that temperature for 1minute.The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 140
,and is maintained at that temperature for 1minute.The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 140 and 250
and 250 ,respectively.Inject the headspace fromReference solution 5into the chromatograph,and record the peak responses as directed forProcedure:the relative retention times are about 0.3for methanol,0.5for isopropyl alcohol,1.0for secondary butyl alcohol,and 1.3for methoxyethanol;the resolution,R,between methanol and isopropyl alcohol is not less than 2.5;and the relative standard deviation determined from individual peak responses from replicate injections is not more than 5%.
,respectively.Inject the headspace fromReference solution 5into the chromatograph,and record the peak responses as directed forProcedure:the relative retention times are about 0.3for methanol,0.5for isopropyl alcohol,1.0for secondary butyl alcohol,and 1.3for methoxyethanol;the resolution,R,between methanol and isopropyl alcohol is not less than 2.5;and the relative standard deviation determined from individual peak responses from replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Using a gas-tight syringe,separately inject equal volumes (about 2mL)of the headspace ofTest solutions 2,3,4,5,andReference solution 5into the chromatograph,record the chromatograms,and measure the areas for the major peaks.Calculate the peak area ratio for each analyte to the internal standard.Plot the peak area ratios obtained from theTest solutions against the quantity of each individual analyte standard added per g of Iohexol.Extrapolate the line joining the points until it intercepts the concentration axis.The distance between this point and the intersection of the axis is the concentration,in mg per g,of methanol,isopropyl alcohol,or methoxyethanol in the portion of Iohexol taken.Not more than 0.005%each of methanol and isopropyl alcohol is found;and not more than 0.002%of methoxyethanol is found.
Limit of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol—
Test solution—
Dissolve about 1g of Iohexol,accurately weighed,in 1.0mLof water.Extract 4times with 2mLof ethyl acetate,and combine the extracts.Dry the combined extracts with anhydrous sodium sulfate.Filter,and wash the filter with a small amount of ethyl acetate.Combine the wash with the filtrate,and concentrate to a volume of 2.0mL,using a warm water bath and a stream of nitrogen.Pass this solution through a membrane filter,and use the clear filtrate.
Standard solution—
Quantitatively dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol in ethyl acetate to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 20µg per mL.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve 1g of Iohexol containing less than 5µg of chloropropanediol in 1mLof water.Quantitatively dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol in ethyl acetate to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 25µg per mL.Add 2.0mLof the ethyl acetate solution to the aqueous solution of Iohexol in a separator,and mix.Transfer the ethyl acetate layer to a separate container,and extract the aqueous layer three additional times with 2mLof ethyl acetate,combining all four extracts.Dry the combined extracts using anhydrous sodium sulfate.Filter,and wash the filter with a small amount of ethyl acetate.Combine the wash with the filtrate,and concentrate and filter as directed underTest solution.
Chromatographic system(see Chromatography á621ñ)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.32-mm ×30-m fused-silica capillary column bonded with a 1-µm layer of phase G46.The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at about 230 and 250
and 250 ,respectively.The carrier gas is helium under 760mm Hg pressure.The column temperature is held at 50
,respectively.The carrier gas is helium under 760mm Hg pressure.The column temperature is held at 50 for 2minutes and is programmed to increase at a rate of 10
for 2minutes and is programmed to increase at a rate of 10 per minute to 200
per minute to 200 .Chromatograph theStandard solution,and record the responses as directed forProcedure:the relative standard deviation of replicate injections is not more than 10%.Chromatograph theSystem suitability solution,and record the responses as directed forProcedure.Calculate the percentage of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol in the portion of Iohexol taken by the formula:
.Chromatograph theStandard solution,and record the responses as directed forProcedure:the relative standard deviation of replicate injections is not more than 10%.Chromatograph theSystem suitability solution,and record the responses as directed forProcedure.Calculate the percentage of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol in the portion of Iohexol taken by the formula:
100(ARC/AST)(CST/CRS),
in whichARCis the response of the analyte peak in the chromatogram obtained from theSystem suitability solution;ASTis the response of the analyte peak in the chromatogram obtained from theStandard solution;CSTis the concentration of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol,in µg per mL,in theStandard solution;andCRSis the concentration of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol,in µg per mL,in theSystem suitability solution:not less than 60%and not more than 90%of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol is found.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 2µL)ofTest solution into the chromatograph,and record the chromatograms.Measure the areas for the major peaks due to the two chloropropanediol isomers,which elute at about 12and 12.5minutes.Calculate the quantity,in µg,of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol in the portion of Iohexol taken by the formula:
100(ASA/AST)(2CST/R),
in whichASAis the total of the peak responses of the two isomers in the chromatograph obtained from theTest solution;ASTis the total of the peak responses of the two isomers in the chromatograph obtained from theStandard solution;CSTis the concentration of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol,in µg per mL,in theStandard solution;andRis the percentage recovery determined underChromatographic system.Not more than 0.0025%of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol is found.
Related compounds—
Solution A—
Use acetonitrile.
Solution B—
Use water.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of a degassed mixture ofSolution AandSolution Bas directed forChromatographic system.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Iohexol RS,USP Iohexol Related Compound A RS,and USP Iohexol Related Compound C RSin water to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 1.5mg per mL,0.0075mg per mL,and 0.0069mg per mL,respectively.
Test solution—
Transfer 75.0mg of Iohexol,accurately weighed,to a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Chromatographic system(see Chromatography á621ñ)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm ×25-cm stainless steel column that contains packing L1.The flow rate is about 1mLper minute.The chromatograph is programmed to provide variable mixtures ofSolution AandSolution B:the percentage ofSolution Aincreases from 1%to 13%at a rate of 0.2%per minute.Chromatograph theSystem suitability solution,and record the peak responses as directed forProcedure:the retention time for theO-alkylated compounds is between 1.1and 1.4relative to 1.0for theexo-isomer of iohexol;the resolution,R,between iohexol related compound Aand iohexol related compound Cis not less than 20.0;and the peak area of iohexol related compound Cis 0.5%±0.1%by comparison to the total area of all the peaks in the chromatogram.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 10µL)of theTest solution into the chromatograph,record the chromatogram,and measure all the peak responses.Calculate the percentage ofO-alkylated compounds and any other individual impurity peak,excluding peaks with a retention time between 0.84(relative to the endo-isomer of iohexol [first main peak])and the endo-isomer of iohexol,in the portion of Iohexol taken by the formula:
100(ri/rs),
in whichriis the response of each impurity;andrsis the sum of the responses of all of the peaks:not more than 0.1%of any individual impurity is found;not more than 0.6%of O-alkylated compounds is found;and the sum of all impurities,other than O-alkylated compounds,is not more than 0.3%.
Assay—
Transfer about 500mg of Iohexol,accurately weighed,to a glass-stoppered,125-mLconical flask.Add 25mLof 1.25Nsodium hydroxide and 500mg of powdered zinc,connect the flask to a reflux condenser,and reflux the mixture for 1hour.Cool the flask to room temperature,rinse the condenser with 20mLof water,disconnect the flask from the condenser,and filter the mixture.Rinse the flask and the filter thoroughly with small portions of water,adding the rinsings to the filtrate.Add 5mLof glacial acetic acid,and titrate with 0.1Nsilver nitrate VS,determining the endpoint potentiometrically.Each mLof 0.1Nsilver nitrate is equivalent to 27.37mg of C19H26I3N3O9.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Andrzej Wilk,Ph.D.,Senior Scientific Associate
Expert Committee:(RMI)Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents
USP28–NF23Page 1043
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.29(6)Page 1908
Phone Number:1-301-816-8305