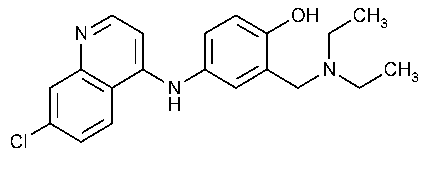
Amodiaquine
Phenol,4-[(7-chloro-4-quinolinyl)amino]-2-[(diethylamino)-methyl]-.
4-[(7-Chloro-4-quinolyl)amino]-a-(diethylamino)-o-cresol [86-42-0].
»Amodiaquine contains not less than 97.0percent and not more than 103.0percent of C20H22ClN3O,calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption á197Kñ—Prepare the standard specimen as follows.Dissolve 20mg of USP Amodiaquine Hydrochloride RSin 10mLof water in a separator,add 1mLof ammonium hydroxide,and extract by shaking with 25mLof chloroform.Draw off and evaporate the chloroform extract,and dry the residue at 105 for 2hours.
for 2hours.
Water,Method Iá921ñ:
not more than 0.5%.
Residue on ignition á281ñ:
not more than 0.2%.
Chromatographic purity—
Standard solutions—
To 20mg of USP Amodiaquine Hydrochloride RSin a glass-stoppered test tube add 1.0mLof chloroform (saturated with ammonium hydroxide),and shake vigorously for 2minutes.Allow the solids to settle,and decant the liquid into a second test tube (Standard solution A).Prepare a second solution by diluting 1.0volume of Standard solution Awith chloroform (saturated with ammonium hydroxide)to obtain 200volumes of solution (Standard solution B).
Test solution—
Dissolve 150mg of Amodiaquine in 10mLof chloroform (saturated with ammonium hydroxide).
Procedure—
Apply 10-µLportions of Standard solution A,Standard solution B,and the Test solutionto a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography á621ñ)coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture.Allow the spots to dry,and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of chloroform (saturated with ammonium hydroxide)and dehydrated alcohol (9:1)until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate.Remove the plate from the developing chamber,mark the solvent front,allow the solvent to evaporate,and examine the plate under short-wavelength UVlight:the chromatograms show principal spots at about the same RFvalue,and no secondary spot,if present in the chromatogram from the Test solution,is more intense than the principal spot obtained from Standard solution B.
Organic volatile impurities,Method Vá467ñ:
meets the requirements.
Solvent—
Use dimethyl sulfoxide.
Assay—
Transfer about 300mg of Amodiaquine,accurately weighed,to a 200-mLvolumetric flask,add 0.1Nhydrochloric acid to volume,and mix.Pipet 10.0mLof the resulting solution into a 1000-mLvolumetric flask,add 0.1Nhydrochloric acid to volume,and mix.Concomitantly determine the absorbances of this solution and a Standard solution of USP Amodiaquine Hydrochloride RSin the same medium having a known concentration of about 15µg per mL,in 1-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 342nm,with a suitable spectrophotometer,using 0.1Nhydrochloric acid as the blank.Calculate the quantity,in mg,of C20H22ClN3Oin the portion of Amodiaquine taken by the formula:
(355.87/428.79)(20C)(AU/AS),
in which 355.87and 428.79are the molecular weights of amodiaquine and anhydrous aminodiaquine hydrochloride,respectively;Cis the concentration,in µg per mL,calculated on the anhydrous basis,of USP Amodiaquine Hydrochloride RSin the Standard solution;and AUand ASare the absorbances of the solution of amodiaquine hydrochloride and the Standard solution,respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Behnam Davani,Ph.D.,MBA,Senior Scientist
Expert Committee:(PA7)Pharmaceutical Analysis 7
USP28–NF23Page 141
Phone Number:1-301-816-8394