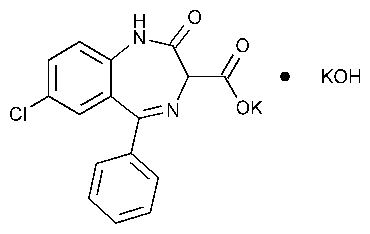
Clorazepate Dipotassium
1H-1,4-Benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid,7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-,potassium salt compound with potassium hydroxide (1:1).
Potassium 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate compound with potassium hydroxide (1:1) [57109-90-7].
»Clorazepate Dipotassium contains not less than 98.5percent and not more than 101.5percent of C16H11ClK2N2O4,calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve under nitrogen in tight,light-resistant containers.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption á197Mñ.
Solution:
7µg per mL.
Medium:
sodium hydroxide solution (1in 2500).
Loss on drying á731ñ—
Dry it in vacuum at 60 for 1hour:it loses not more than 0.5%of its weight.
for 1hour:it loses not more than 0.5%of its weight.
Heavy metals,Method IIá231ñ:
0.002%.
Related compounds—
[NOTE—Once the solutions are prepared,they are unstable and should be used immediately.]
Diluting solution—
Prepare a solution by dissolving 4g of potassium carbonate in 100mLof water.
Standard solution A—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Clorazepate Dipotassium RSand dilute stepwise with Diluting solutionto obtain a solution having a concentration of 0.1mg per mL.
Standard solution B—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 10mg of USP2-Amino-5-chlorobenzophenone RSto a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dissolve in and dilute with acetone to volume,and mix.Dilute 10.0mLof this solution with acetone to 50.0mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of about 100mg of Clorazepate Dipotassium in 5.0mLof Diluting solution.
Procedure—
Apply separately 5µLof the Test solutionand 5µLof each Standard solutionto a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography á621ñ)coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture.Allow the spots to dry,and develop the chromatograms in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of chloroform and acetone (85:15)until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate.Remove the plate from the developing chamber,mark the solvent front,and allow the solvent to evaporate.Examine the plate under short-wavelength UVlight,and compare the intensities of any secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test solutionwith those of the principal spots in the chromatograms of Standard solution A.No secondary spot from the chromatogram of the Test solutionis larger or more intense than the principal spot obtained from Standard solution A(0.5%).Successively spray the plate with a freshly prepared 1%solution of sodium nitrite in 1Nhydrochloric acid.Dry the plate in a current of air and spray with a 0.4%(w/v)solution of N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in alcohol.Any violet-colored spot present in the chromatogram of the Test solutionis not greater in size or intensity than the principal spot obtained from Standard solution B(0.1%),and the sum of the intensities of all secondary spots obtained by both visualization techniques from the Test solutioncorresponds to not more than 1%.
Organic volatile impurities,Method Iá467ñ:
meets the requirements.
Assay—
Transfer about 150mg of Clorazepate Dipotassium,accurately weighed,to a 250-mLbeaker,add 100mLof glacial acetic acid,and stir until dissolved.Titrate with 0.1Nperchloric acid VS,determining the endpoint potentiometrically,using a glass electrode and a calomel electrode containing a 1in 100solution of lithium perchlorate in glacial acetic acid.Perform a blank determination (see Titrimetry á541ñ),and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 0.1Nperchloric acid is equivalent to 13.63mg of C16H11ClK2N2O4.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Salvador C.Salado,M.S.,Scientist and Latin American Liaison
Expert Committee:(PA3)Pharmaceutical Analysis 3
USP28–NF23Page 517
Phone Number:1-301-816-8165