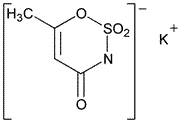
Add the following:
6-Methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt.
3,4-Dihydro-6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt [55589-62-3].
»Acesulfame Potassium contains not less than 99.0percent and not more than 101.0percent of C4H4NO4SK,calculated on the dried basis.
USP Reference standards á11ñ—
USP Acesulfame Potassium RS.
Identification—
A:Infrared Absorption á197Kñ.
B:
Asolution (1in 10)responds to the tests for Potassium á191ñ.
Acidity or alkalinity—
Dissolve 4.0g in 20mLof carbon dioxide-free water,add 0.1mLof bromothymol blue TS.If the solution is yellow,not more than 0.2mLof 0.01Nsodium hydroxide is required to produce a blue color.If the solution is blue,not more than 0.2mLof 0.01Nhydrochloric acid is required to produce a yellow color.
Loss on drying á731ñ—
Dry at 105 for 3hours:it loses not more than 1.0%of its weight.
for 3hours:it loses not more than 1.0%of its weight.
Limit of fluoride—
[NOTE—Use plasticware throughout this test.]
Buffer solution—
Dissolve 210g of citric acid monohydrate in 400mLof water.Adjust with concentrated ammonia to a pHof 7.0,dilute with water to 1000mL,and mix(Solution A).Dissolve 132g of monobasic ammonium phosphate in water,dilute with water to 1000mL,and mix(Solution B).To a suspension of 292g of edetate disodium in about 500mLof water,add about 200mLof ammonium hydroxide,and mix to dissolve(Solution C).Adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pHbetween 6and 7,dilute with water to make 1000mL,and mix.Mix equal volumes of Solution A,Solution B,and Solution C,and adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pHof 7.5.
Standard stock solution—
Weigh accurately 0.442g of sodium fluoride,previously dried at 300 for 12hours,into a 1-Lvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Store the solution in a closed plastic container.Immediately before use,pipet 5mLof this solution into a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Each mLof this solution contains 10µg of fluoride ion.
for 12hours,into a 1-Lvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Store the solution in a closed plastic container.Immediately before use,pipet 5mLof this solution into a 100-mLvolumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.Each mLof this solution contains 10µg of fluoride ion.
Standard solutions—
Into separate 50-mLvolumetric flasks,pipet 0.5,1.5,5,and 15mLof the Standard stock solution,add 15.0mLof Buffer solutionto each volumetric flask,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Test solution—
Place 1g of Acesulfame Potassium,accurately weighed,in a 50-mLvolumetric flask,dissolve in water,add 15.0mLof Buffer solution,dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Procedure—
Concomitantly measure the potential (see Titrimetry á541ñ),in mV,of theStandard solutions and the Test solution,with a suitable pHmeter equipped with a fluoride-specific ion electrode and a silver-silver chloride reference electrode.When taking the measurements,transfer the solution to a 25-mLbeaker,and immerse the electrodes.Insert a polytef-coated stirring bar into the beaker,place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top,and allow to stir until equilibrium is attained (about 1to 2minutes).Rinse,and dry the electrodes between measurements,taking care not to scratch the crystal in the flouride-specific ion electrode.Measure the potential of each Standard solution,and plot the fluoride concentration,in µg per mL,versus the potential,in mV,on semilogarithmic paper.Measure the potential of the Test solution,and determine the fluoride concentration from the standard curve,in µg per mL.Calculate the percentage of fluoride in the portion of Acesulfame Potassium taken by the formula:
5(C/W),
in which Cis the fluoride concentration,in µg per mL,from the standard curve;and Wis the weight,in mg,of Acesulfame Potassium taken to prepare the Test solution:not more than 0.0003%of fluoride is found.
Heavy metals,Method Iá231ñ:
10µg per g.
Chromatographic purity—
Tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate solution—
Dissolve 3.3g of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate in 1Lof water,and mix.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of Tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate solution and acetonitrile (3:2),filter,and degas.Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography á621ñ).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve suitable quantities of USP Acesulfame Potassium RSand ethylparaben in water to obtain a solution containing about 2µg per mLof each.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Acesulfame Potassium RSin water,and dilute quantitatively,and stepwise if necessary,with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.2µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100mg of Acesulfame Potassium,accurately weighed,to a 10-mLvolumetric flask,dissolve in and dilute with water to volume,and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography á621ñ)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 227-nm detector and a 4.6-mm ×25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1.The flow rate is about 1.0mLper minute.Chromatograph the System suitability solution,and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure:the resolution,R,between acesulfame potassium and ethyparaben peaks is not less than 2.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20µL)of the Standard solutionand the Test solutioninto the chromatograph,record the chromatograms for a run time not less than 3times the retention time of the acesulfame potassium peak,and measure the area responses of the peaks:the response of any peak at a retention time other than that of acesulfame potassium in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solutiondoes not exceed the response of the acesulfame potassium peak in the chromatogram obtained from the Standard solution (0.002%).
Assay—
Dissolve about 150mg of Acesulfame Potassium,accurately weighed,in 50mLof glacial acetic acid,and titrate with 0.1Nperchloric acid VS,determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see Titrimetry á541ñ).Perform a blank determination,and make any necessary correction.Each mLof 0.1Nperchloric acid is equivalent to 20.12mg of C4H4NO4SK. NF23
NF23
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison:Karen A Russo,Ph.D.,Scientist
Expert Committee:(EMC)Excipients:Monograph Content
USP28–NF23Page 2947
Pharmacopeial Forum:Volume No.30(2)Page 591
Phone Number:1-301-816-8379